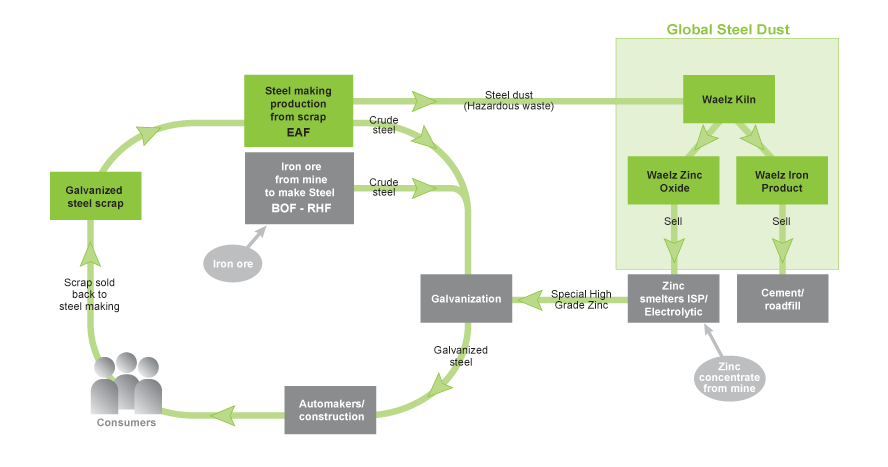
Recycling Steel Dust
Zinc-coated galvanized steel scrap is the most widely used feedstock for Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) steel production. World crude steel production reached 1,66 billion metric tons for the year 2014, up by 3.9% compared to 2013 (World Steel Association). Around 26% of crude steel is produced using the EAF technology.
During the EAF process, the high temperatures required to melt the feed material produce a zinc byproduct (EAF dust) that leaves the furnace along with the off-gases. The gases are filtered and the EAF dust is collected in bag houses.
The EAF dust waste steam is considered a hazardous material due to the potential for the heavy metals to leach into the ground, contaminating ground water and sewage systems.
The EAF dust generated by steel mills can be recycled in an economically viable way using the Waelz Kiln technology. The recycling process is part of the larger steel industry loop that allows the reuse of two important natural resources - zinc and iron.
GSD’s Role in the Recycling Loop
Historically, in most developed countries, manufacturers landfilled EAF dust at a significant financial cost. However, increased landfill costs, governmental, environmental and social pressures placed on steel producers are encouraging steel companies to take advantage of sustainable disposal options that allow for the recovery of valuable recyclable components, such as zinc and iron units.
Global Steel Dust (GSD) provides steel companies a viable option to landfilling. Steel companies can be assured hazardous waste is treated safely, reliably and within the environmental laws of each jurisdiction in which GSD operates. The opportunity to recycle EAF dust reduces the steel companies' cost of disposal and closes the industry loop, resulting in an environmentally friendly outcome.
End Uses of Zinc
Waelz Zinc Oxide is the main product of recycling EAF dust utilizing the Waelz Kiln technology. This product is sold to zinc smelters as an alternative to traditional zinc concentrates from mines. The zinc smelters produce pure zinc ingots or other high purity zinc products that are either sold to the steel industry for galvanization purposes or sold to other end-users for pigments, tires, chemicals or medicines.
The automotive industry has seen an increased use of zinc as an anticorrosion agent for steel. Because galvanized steel scrap is mostly recycled as EAF steel production feedstock, the increased amount of EAF dust with higher zinc content will continue to rise.
Source: ILZSG

